Permissions and Access Control
Types of access on files read (r): user can view the contents of the file write (w): user can change the contents of the file execute (x): user can execute or run the file if it is a program or script
Types of access on directories read (r): user can list the contents of the directory (e.g., using ls) write (w): user can create files and sub-directories inside the directory execute (x): user can enter that directory (e.g., using cd)
File Permissions
you can use ls -l to see the level of permission on file and directories. in this photo you can see the meaning of each field: 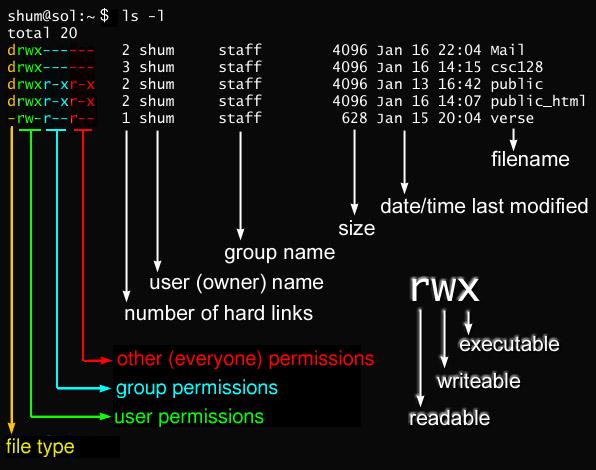
Change Permission
There are times that you want to change the access to a file. For example, there is a file and you want to share it with a user, a user group, or to the public like sharing a file on your website. Sometimes also you need to give your file a execution permission to be able to run it such as bash files. to change the access contorl on a file, use chmod command.
There are two most common ways of chaning permission on a file or directory. First, using + or - ro add or remove permission for r (reading), w (writing), and x (execution).
chmod +x file.sh # gives execution to a file
chmod -w book.txt # remove writing permission of book.txt. this file is a read-only file now.
chmod -r book.txt # remvoe reading permission of book.txt. you can not read this file anymore.
the second way of changing the permission is using numbers. each file permission is a combination of rwx. think of it as a three bit number and it gives you a number from 0 to 7. for example, 000 is 0 and that means rwx are 000. Which means no read, no write, no permission. if you want to give full access to a file, user 111 which is 7. This means read, write, and execute permissions. Then you can make a three digit number for user, group, and others in order. for example, 755 means 7 (111) for user itself, 5 (101) for user group, and 5 (101) for the public.
chmod 755 book.txt # write what this does
chmod 644 book.txt # write what this does
umask
umask value: decides the default permissions for new files
umask # to see the current umask value
touch t1 # create a new file called t1 with current defaule umask value
umask 0000 # change umask value to 0000
touch t2 # create a new file called t2 with current umask value
umask 0777 # change umask value to 0777
touch t3 # craete a new file called t3 with current umask value
ls -l # check the file persmission for t1, t2, and t3
acl
acl (Access Control List) is a package for managing the access control list. it provides a fine grained access control features. it assigns permissions to individuals users/groups and coexist with the traditional permission model.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install acl # install acl if is not intalled by default on your system
to get the current permission, use the getfacl:
getfacl book.txt
to set permission, use setfacl. explain how to use setfacl
running command with privilege
Using sudo
sudo is installed by default in the shell. however, if is not installed on docker version, instll it using apt install sudo.
It is not recommended to run commands using a root shell. Instead, a user must be logged in using a user account and then use sudo to run individual commands that need root privilege. to run a command in root mode while you are in your user mode, use sudo.
sudo chmod +x book.txt # a user typically requires to runs chmod with needs sudo permission to change a file's access control
sudo apt update # package management requires having sudo access level
sudo -u bob id # Run command using another user (instead of root, default)
The Password File
Each entry contains a user account information Password is not stored here (used to be) The last field of each entry is the First Command After Login
The Shadow File
Store password, why not use /etc/password anymore? Structure for each entry
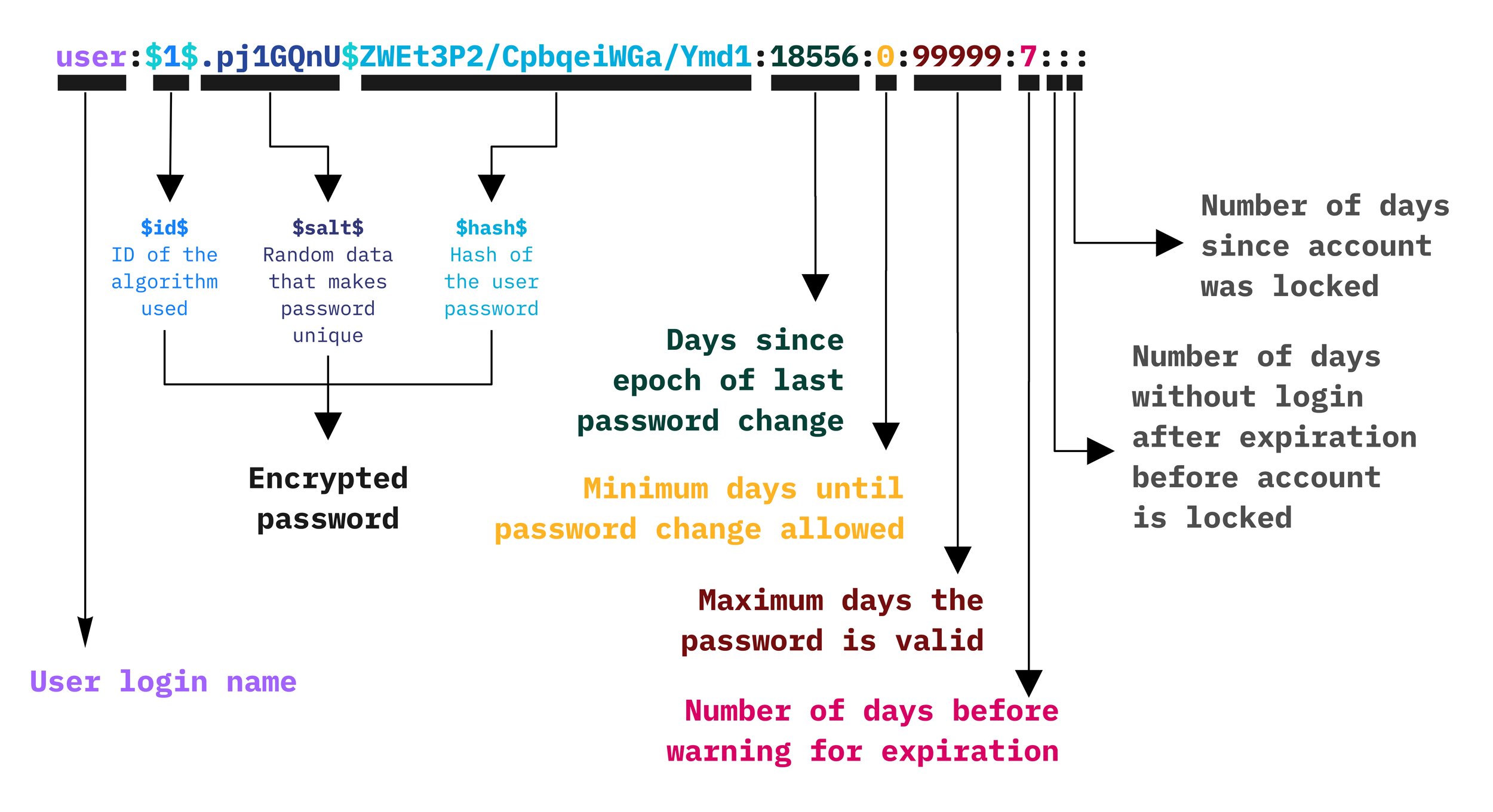
-
Example usage:
cat /etc/shadow
The Purpose of Salt Defeat brute-force attacks dictionary attack, rainbow table attack store the accounts with the same password differently
Note. Putting an invalid value in the password field cause the the root account is locked